Table of Contents
Prerequisites
- Required services: FortiGate with SSL VPN enabled, Microsoft Entra ID tenant
- A valid public FQDN (sub.domain.tld) for the FortiGate SSL VPN certificate
- A working certificate on the FortiGate (Let’s Encrypt, public CA, etc.)
Add FortiGate SSL VPN in Entra ID
- Enterprise Applications → Add from Gallery → Select FortiGate SSL VPN
Configure Basic SAML Settings in Entra ID
- Identifier (Entity ID)
- Reply URL (ACS)
- Sign-on URL
- Logout URL
- Attribute & Claim mappings (username, group)
- Download the SAML Base64 Signing Certificate
SAML Claim Mapping (Azure → FortiGate)
FortiGate is strict about SAML attribute names. The attributes defined in Azure must match exactly the attributes that FortiGate expects under:
set user-name set group-name
Required Claims in Entra ID
Under Single Sign-On → User Attributes & Claims:
Add this claim (FortiGate requires the literal name)
- Claim name:
username, source:user.userprincipalname
Edit the existing “groups” claim so that it sends Group Object IDs (not display names).
- The expected claim name must be
group
must be group
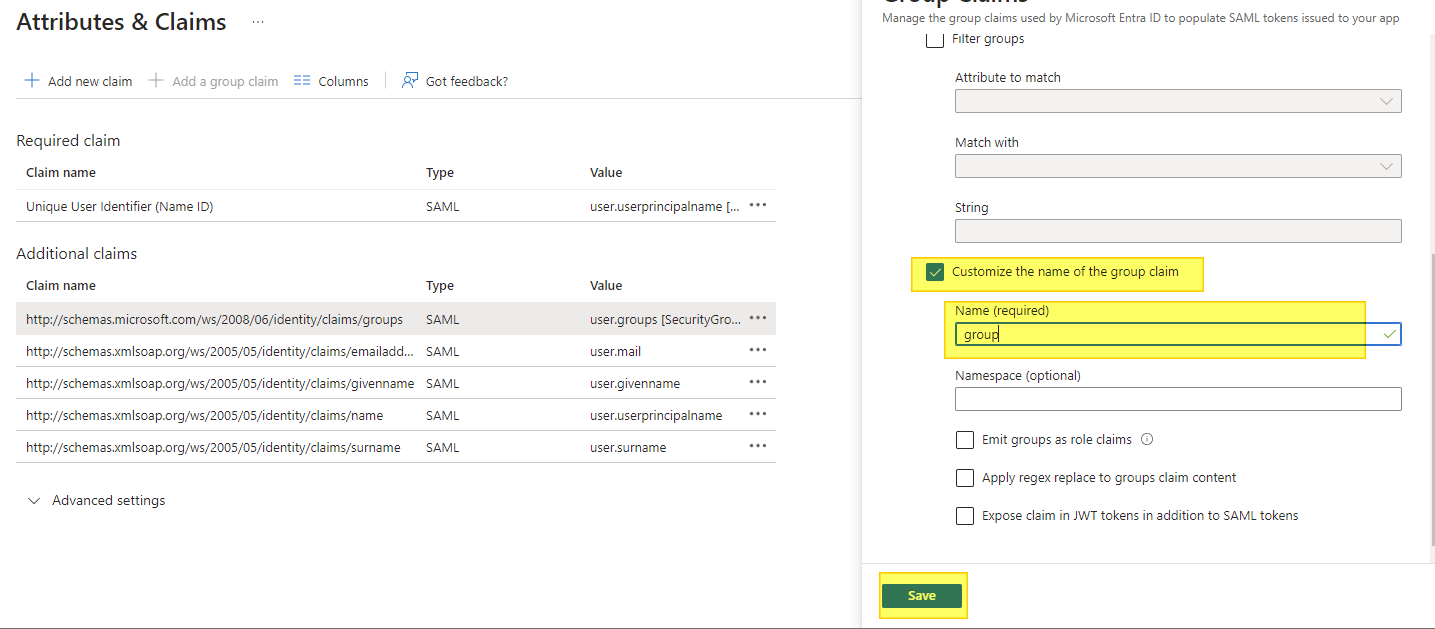
This ensures that the SAML token contains:
username = user@domain group = <Azure AD Group Object ID>
Why this matters
FortiGate matches SAML attributes using the `user-name` and `group-name` fields in the IdP configuration:
set user-name "username" set group-name "group"
If the Azure claim sends the wrong attribute or the Object ID doesn't match exactly, FortiGate will not associate the session with the group, and the VPN connection will be denied.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/saas-apps/fortigate-ssl-vpn-tutorial
Create Test User and Security Group in Entra ID
- Create test user
- Assign user to the FortiGate SSL VPN enterprise app
- Create Security Group (e.g., *FortiGateAccess*)
- Copy the Object ID (used later in FortiGate group matching)
Upload Certificate to FortiGate
- Import the SAML IdP certificate into FortiGate
- Rename the certificate if needed for clarity
Configure FortiGate SAML Settings (CLI)
- Define the SAML IdP (`config user saml`)
- Configure entity-id, SSO URLs, IdP URLs, certificate, and attribute mapping
config user saml
edit azure
set cert "<FortiGate VPN Server Certificate Name>"
set entity-id "https://vpn.my.org:10443/remote/saml/metadata"
set single-sign-on-url "https://vpn.my.org:10443/remote/saml/login"
set single-logout-url "https://vpn.my.org:10443/remote/saml/logout"
set idp-entity-id <Azure AD Identifier>
set idp-single-sign-on-url <Azure Login URL>
set idp-single-logout-url <Azure Logout URL>
set idp-cert <Azure SAML Base64 Certificate Name>
set user-name username
set group-name group
next
end
Configure FortiGate User Group
- Create a user group mapped to Azure SAML IdP
- Match against the Azure AD Security Group Object ID
config user group
edit AAD-FortiVPN
set member azure
config match
edit 1
set server-name azure
set group-name 343744cd---GROUP-ID---67bb7e68
next
end
next
end
Configure SSL VPN Portals and Firewall Policy
- Create SSL VPN portal(s)
- Assign the portal to the SAML group
- Add firewall policies allowing access from the SAML user group
Optional: Multiple SSL VPN Realms
- Enable the SSL-VPN Realms feature
- Create multiple realms (e.g., *FullTunnel*, *SplitTunnel*)
- Assign specific portals and firewall policies per realm
FortiClient Setup (Optional)
- Configure FortiClient for SSL VPN using SAML SSO
- Ensure FQDN and port match the FortiGate SAML configuration
Testing and Validation
- Use Azure → “Test” SSO functionality
- Direct login to FortiGate VPN portal Web UI
- Launch from MyApps portal tile
- Use FortiGate debugging commands:
diagnose debug application sslvpn -1 diagnose debug application samld -1 diagnose debug console timestamp enable diagnose debug enable
To stop debugging:
diagnose debug reset diagnose debug disable
FortiClient connection stages:
- 20% – TCP connection
- 40% – SAML authentication
- 80% – Tunnel negotiation
- 100% – Connected
For example, if it fails at 40%, SAML assertion is not validated.
Troubleshooting Notes
- Re-download metadata/cert when FQDN or port changes
- Signature validation requirements changed in FortiOS 7.2.12 / 7.4.9 / 7.6.4
- Common errors (e.g., *“Signature element not found”* from FortiGate)
- Adjust group claim: ensure the Azure AD group appears in the SAML assertion
