This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Veeam Components Overview
Veeam Backup & Replication is a comprehensive solution for data protection across various environments, including cloud, virtual, and physical systems.
Core Components
- Backup Server - The central management component, installed on a Windows-based machine or VM.
- Backup Proxy - Handles data processing and transfer, optimizing backup performance.
- Backup Repository - Storage location for backup files, supporting various repository types.
Additional Components
- Backup & Replication Console - Client-side interface for managing backup operations.
- Veeam Data Movers - Responsible for data retrieval, deduplication, compression, and storage.
- Gateway Server - Bridges the backup server and repository, required for certain storage types.
- Mount Server - Facilitates restores involving guest OS files and application items.
Backup File Types
.VBM- Metadata file for backup management..VBK- Full backup file (active or synthetic)..VIB- Incremental backup file.
Proxy Types
- VMware Proxy - Default role on the backup server, can be installed on other Windows/Linux servers.
- General Purpose Proxy - Used for NAS, file shares, and physical server backups.
- Hyper-V Off-Host Proxy - Reduces load on production Hyper-V hosts by handling backup operations separately.
For more details, visit the [Veeam Community Resource Hub](https://community.veeam.com/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-163/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-step-2-1-veeam-components-and-infrastructure-requirements-10012).
Backup Repositories and Transport Modes
Veeam Backup & Replication supports various storage options and transport methods to optimize data protection and recovery.
Backup Repository Types
- DAS (Direct Attached Storage) - Includes USB, eSATA, and raw device mapping (RDM).
- Linux Hardened Repository - Provides immutability and security against ransomware and insider threats.
- Object Storage - Supports AWS S3, Azure Blob, IBM Cloud, and S3-compatible storage.
- SAN (Storage Area Network) - Enables direct access via hardware, HBA, or iSCSI initiators.
- SMB/NFS - Supports SMB 3.0+ and NFS shares with proper permissions.
- Tape - Fully integrated native tape support for long-term storage.
- Deduplication Appliances - Hardware-based storage optimization with built-in deduplication and compression.
- External Repositories - Read-only repositories for cloud-to-on-premises data migration.
Transport Modes
- Direct Storage Access - Provides the highest performance by accessing storage directly.
- Virtual Appliance (HotAdd) - Uses VMware SCSI HotAdd for efficient datastore access.
- Network Mode (NBD/NBDSSL) - Transfers data over TCP/IP, offering broad compatibility.
- Backup from Storage Snapshots - Reduces impact on production environments by leveraging storage snapshots.
vPower NFS Service Features
The vPower NFS Service is a Microsoft Windows service that runs on a Microsoft Windows machine and enables this machine to act as an NFS server.
- SureBackup - Verifies backup integrity.
- SureReplica - Ensures replica reliability.
- Instant Recovery - Enables rapid VM recovery.
- Staged Restore - Facilitates compliance-driven restores.
- Universal Application-Item Recovery (U-AIR) - Allows granular application recovery.
- Multi-OS Guest OS File Restore - Supports file-level recovery across different operating systems.
For more details, visit the [Veeam Community Resource Hub](https://community.veeam.com/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-163/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-step-2-2-backup-repositories-and-transport-modes-10013).
Deployment Options
Veeam Backup & Replication can be deployed in various environments, including on-premises, private, public, and hybrid clouds. The prerequisites and functionality remain consistent across these environments.
Deployment Types
- On-Premises Deployment - Scales from simple installations to complex infrastructures.
- Service Provider Deployment - Used by providers offering Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS).
- Cloud Workload Deployment - Protects workloads running on cloud VMs.
Simple Deployment
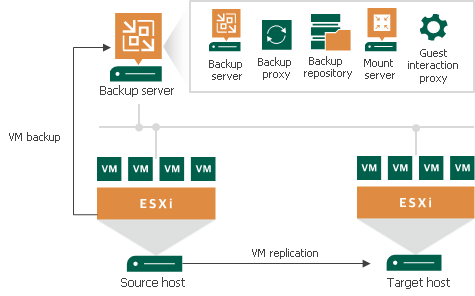
- All components (server, proxy, repository) installed on a single machine.
- Suitable for small-to-medium businesses (SMBs) needing local backup copies.
- Can be deployed in public clouds like Azure, AWS, and others.
- Backup data can be stored in disk-/file-based repositories or object storage.
Advanced Deployment
- Supports horizontal scaling to match data processing needs.
- Distributes backup workloads across multiple infrastructure components.
- Automated installation simplifies deployment and maintenance.
- Ideal for large environments requiring flexible storage solutions.
For more details, visit the [Veeam Community Resource Hub](https://community.veeam.com/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-163/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-step-2-3-deployment-options-10014).
Business Considerations for Veeam Deployments
Understanding key business considerations ensures a successful Veeam Backup & Replication deployment. These principles help optimize backup strategies, security, and recovery objectives.
The 3-2-1-1-0 Rule
A best practice for data protection:
- (3) Copies of Data - Maintain primary data and two backup copies.
- (2) Different Media - Store backups on separate storage types (e.g., local disk + cloud).
- (1) Offsite Copy - Ensure at least one backup is stored remotely.
- (1) Offline/Air-Gapped Copy - Use immutable storage (e.g., Hardened Linux Repository, Object Lock).
- (0) Errors - Automate testing and verification (SureBackup, SureReplica).
Key Backup Considerations
- Backup Window - Schedule backups outside business hours to minimize impact.
- Backup Type - Choose between incremental (efficient) or full (comprehensive) backups.
- Storage Optimization - Enable compression and deduplication to reduce storage usage.
- Data Encryption - Secure backups with encryption at rest and in transit.
- Bandwidth Throttling - Limit network usage for WAN replication.
- Repository Optimization - Match storage type to backup frequency (e.g., high-performance storage for frequent backups).
- Backup Copy Jobs - Create offsite copies for disaster recovery.
- Scale-out Backup Repository (SOBR) - Automate storage tiering and load balancing.
Retention Strategies
- Short-Term Retention - Locally stored restore points for quick recovery.
- Forever-forward incremental - Efficient but not compatible with SOBR move functionality.
- Forward incremental - Includes periodic full backups for better chain management.
- Long-Term Retention - Weekly, monthly, yearly restore points (GFS policy).
- GFS (Grandfather-Father-Son) - Assigns flags to full backups for archival.
- Cloud Tiering - Moves older backups to object storage.
Recovery Objectives
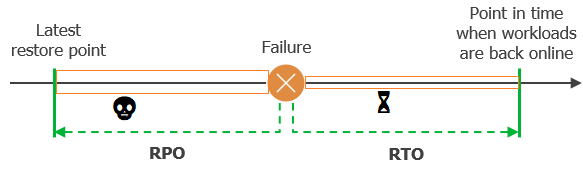
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) - Defines acceptable data loss period.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) - Determines downtime tolerance.
- Disaster Recovery Planning - Establish offsite backups, restore processes, and testing.
Security Considerations
- Physical Security - Restrict access to backup infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Hardening - Implement role-based access control (RBAC).
- Network Segmentation - Separate backup traffic from production networks.
- Immutability & Air-Gapped Storage - Protect against ransomware with offline backups.
- Backup Verification - Schedule SureBackup jobs to validate recoverability.
For more details, visit the [Veeam Community Resource Hub](https://community.veeam.com/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-163/onboarding-for-veeam-data-platform-step-2-4-business-considerations-10015).
